How to Meet the Financial Requirements for a Marriage-Based Green Card
Marriage green cards, which are obtained by marrying a U.S. citizen or permanent resident, are a way for many cross-border lovers to realize their dream of reunification. However, U.S. immigration law requires thatApplicants must provide a financial guarantee that they will not be a public charge while living in the U.S.. This requirement is essential to ensure that new immigrants and their families can become self-sufficient.
01Why do I need to provide a financial guarantee?
When a U.S. citizen or green card holder applies for a green card for a beneficiary (overseas relative, company employee, etc.), the U.S. government requires that the U.S. citizen or green card holder have a certain level of financial strength in order to prevent the beneficiary from becoming a burden on the public after immigrating to the U.S. The U.S. government requires that the U.S. citizen or green card holder have a certain level of financial strength, and that the person acting as the sponsor has the ability to provide the beneficiary with financial support for the beneficiary's work and life in the United States.
02How much income is required for financial sponsorship?
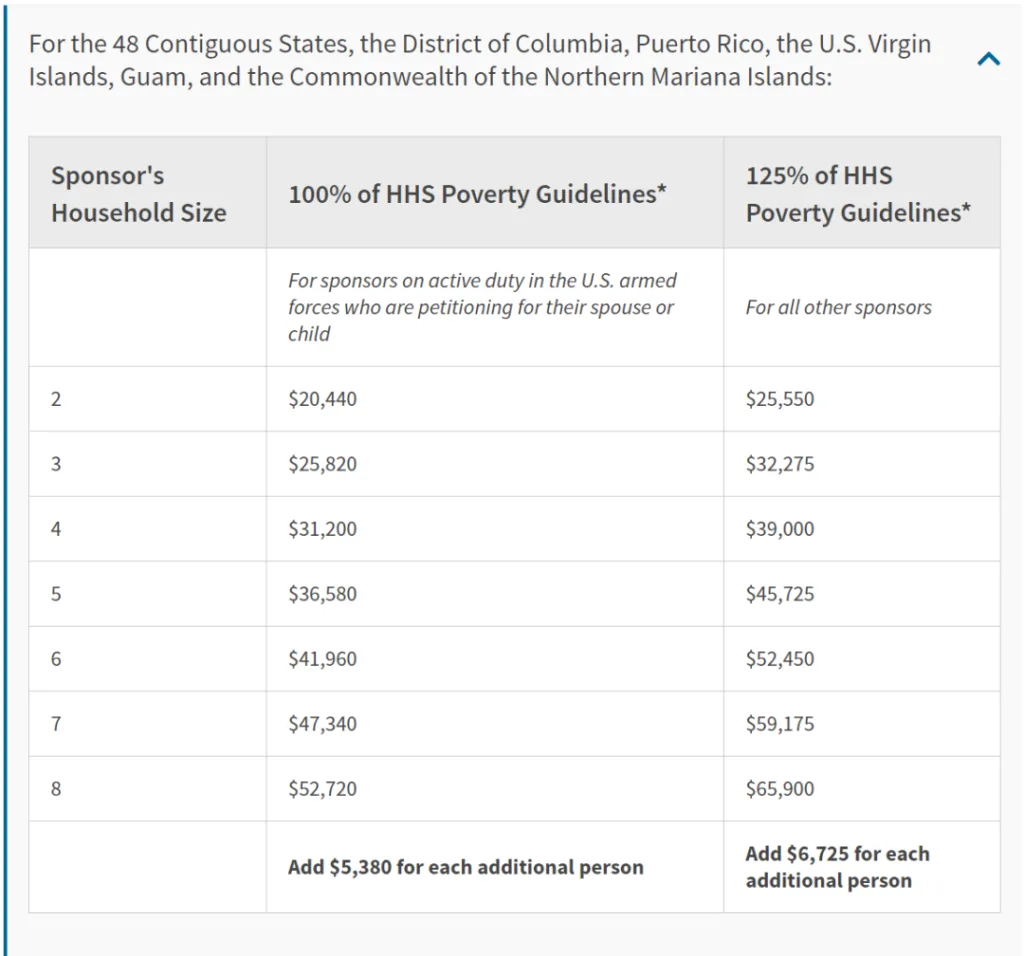
The sponsor of a green card applicant must have an income of 1,251 TP3T or more of the current year's Federal Poverty Level (FPL). For a sponsor who is serving in the U.S. military and is applying for a green card for his or her spouse or children, the income must be at or above the Federal Poverty Level of 1001 TP3 T. If there are more than two people, the income must be at the poverty level for the Sponsor's Household Size.
Additionally, when applying for a marital green card, the beneficiary's income can be included in the U.S. applicant's household income as long as he or she holds an immigrant visa that allows him or her to legally work within the United States. However, the beneficiary must maintain legal work status at all times during the green card application process. If he fails to renew his work card in a timely manner or if his immigration status is about to expire, then his income cannot be included in the U.S. petitioner's household income.
For example, if Mr. K has a family of 4 and he is applying for immigration for his mother, according to the 2024 Federal Poverty Guidelines (refer to the chart below) then his Sponsor's Household Size would be 5, which means he needs to reach $45,725.
03What if the financial sponsor's income is not enough for the guarantee line?
According to the relevant federal regulations, when the income of the financial sponsor is not enough to meet the sponsorship line, the applicant can seek a joint financial sponsor. In other words, when applying for a marriage green card, if the applicant's family income fails to meet the minimum standards set by the immigration law, the applicant may seek to supplement the family income with a qualified beneficiary, a co-sponsor. However, the assets of the joint financial sponsorTotal net worth must be greater than or equal to 5 times the difference between the sponsor's income and the federal poverty level of 125% to which their family size belongs. In addition, assets such as real estate or deposits in the applicant's name can also be used as a way to supplement income. But in general, we stillSuggested for everyone with a steady incomeGo ahead and apply.
property deduction:
The guarantor can utilize his or her own property as proof of assets, but you will be required to provide a little bit of documentation of the property tax land paid on the property in the United States. In addition, it is important to note thatUSCIS prefers sponsors to use liquid assets rather than fixed assets. Because fixed assets such as property are less liquid, when using property as an asset, the net value of the property must be deducted from the loan on the property in order for it to be used as a secured asset, and it is usually necessary to divide this net value by five to calculate the annual income contribution.
In addition, if the amount of the property credit happens to meet the requirements, the USCISReplacement documents may be required due to mobility issues of the property, unless the property credit amount is higher, it may still not be approved.
Property owners are required to pay the governmentProperty tax, which is based on the assessed value of the property. The government records the assessed value of the property on an official document, which is often referred to as a property tax bill.
In order to calculate the net value of the property that can be used for financial security, the applicant needs to follow the steps below:
1. Determine the assessed value of the property: Check the property tax bill to find the official government assessed value of the property.
2. Less outstanding loans: Subtract any outstanding mortgage balance from the assessed value of the property.
3. Calculation of annual income supplement: Divide the net value of the property by 5 to get an amount that can be used as an annual income supplement for financial security.
For example, if the applicant's property has an assessed value of $500,000 and they have an outstanding mortgage of $100,000, the equity in their property would be $400,000. Dividing this $400,000 by 5, as calculated above, equals $80,000. Therefore, the applicant can use this $80,000 as an annual income supplement to their financial guarantee.
Stock Deduction:
Stocks can also be used as an asset to supplement financial sponsorship. However, USCIS does not usually calculate the value of stocks directly as income, but ratherAdditional proof may be required to show the past returns of these stocks and their liquidityThe